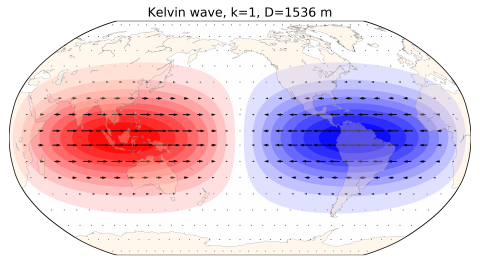
Horizontal structure of the n=0 eastward-propagating inertia-gravity mode on the sphere, Kelvin wave.
Geopotential height is scaled by the maximal height. Colours vary between -1 and +1 with positive/negative perturbations in red/blue.
Wind components are scaled by the maximal wind speed. The equivalent depth is 1536 meters.
Kelvin wave is the slowest eastward-propagating eigensolution of the linearized primitive equations on the sphere, associated with a large part of atmosphere and ocean variability in the tropics. Together with the MRG wave, Kelvin wave fills the frequency gap between the Rossby and inertia-gravity modes in the tropics.
In the case of linearized equations on the equatorial beta-plane, the Kelvin wave is sometimes denoted n=-1 eastward-propagating inertia-gravity mode.
Geopotential height is scaled by the maximal height. Colours vary between -1 and +1 with positive/negative perturbations in red/blue.
Wind components are scaled by the maximal wind speed. The equivalent depth is 1536 meters.
Kelvin wave is the slowest eastward-propagating eigensolution of the linearized primitive equations on the sphere, associated with a large part of atmosphere and ocean variability in the tropics. Together with the MRG wave, Kelvin wave fills the frequency gap between the Rossby and inertia-gravity modes in the tropics.
In the case of linearized equations on the equatorial beta-plane, the Kelvin wave is sometimes denoted n=-1 eastward-propagating inertia-gravity mode.